The Industrial Internet of Things, or IIoT, mainly refers to an industrial framework where a large number of machines or devices are connected and synchronized through software tools.
Industrial IoT devices range from complex industrial robots to tiny environmental sensors. For a large scale, IIoT is an element of Industry 4.0, and it requires low maintenance along with the low cost to operate in real-time in challenging environments.
Generally, companies use IIOT projects to save on internal costs. The commonly used applications of IIoT are smart factories, smart metering, smart grid, and many more. Let us have a clearer vision of industrial IoT and the significant elements that have contributed to its emergence.
- What Is Industrial IoT (IIoT)?
- Historical Overview of IIot
- Differentiating IIoT vs. IoT technology
- How Industrial IoT Works?
- Key Considerations of IIoT implementation
- Advantages of the Industrial Internet of Things
- What are the Risks of IIoT Infrastructure?
- Importance of IT in Industrial IoT
- Exploring the Industrial IoT Use Cases in Diverse Domains
- Examples of Industrial IoT, along with their Applications by Leading Companies
- Contemplating the Future of IoT Devices!
Industrial IoT denotes the implementation of IoT capabilities in the industrial and manufacturing sectors. It enables the concept of machine-to-machine (M2M), connecting each smaller to a larger device within an industrial setup, with the objective of boosting productivity and efficiency.
IIoT utilizes advanced sensors, software, and machine learning functionalities to track, gather, and evaluate large amounts of operational data while performing each task. Additionally, it enables automation, saving time and resources for organizations.
Experts also define IIoT as the process of interconnecting every machine that contributes to industrial operations. Through continuous real-time data assessment and integration, Industrial IoT intends to initiate quick troubleshooting and address even minor errors.
The inception of Industrial IoT was marked by the invention of the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) in 1968 by Richard E. Morley. The mechanism enabled advanced control of each element in the industrial process. Later on in 1975, the introduction of the first DCSs allowed adaptable task regulation in an entire manufacturing environment.
In 1980, the concept of IIoT advanced alongside the emergence of Ethernet. During this time, the idea of M2M received prominence, highlighting a promising future of internet-enabled and inter-connected devices. Finally, in the late 1990s, IoT devices became a topic of discussion among tech experts following the radio-frequency identification by Kevin Ashton.
Gradually, the potential of IoT was integrated for industrial purposes, boosting device connectivity. Consequently, practitioners integrated cloud computing for better M2M performance. The fourth Industrial Revolution, or Industry 4.0, has been a cornerstone for the evolution of industrial IoT. Continuous tech developments and their implementation in the manufacturing sector shall strengthen IIoT even further in the upcoming years.
| IoT | IIoT | |
| Utility | It is mainly designated for individual customers, which can be used in homes and offices. | It is used in commercial areas, that is, industries. |
| Security | Security is not an issue in IoT in comparison to IIoT, as it does not include handling industrial processes. | Security is a major concern in IIoT as it includes organizations and businesses on a large scale. |
| Degree of Application | It uses an application with low-risk impact. | It uses more sensitive and precise sensors. |
| Cost | It is less expensive and such technology has been introduced by various companies. | It is more expensive than IoT as it has sensitive devices and industrial applications. |
IIoT depends on several connected devices, sensors, and other elements. Appropriate implementation and usage of each component are essential for the proper operation of IIoT infrastructure.
Primarily, organizations are required to integrate compatible devices and sensors with M2M capabilities. There are specified equipment, especially designed for automated industrial operations. After integrating the devices, organizations ensure strong connectivity between them. For this purpose, a network facility, like 5G, is adopted. The following stage includes the implementation of cloud or edge computing functionalities.
Cloud and edge computing offers high flexibility and adaptability while storing and processing large amounts of data. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are two unavoidable components of industrial IoT. These mechanisms assist in model formulation and predictive analytics, which contribute to effective industrial task execution.
The final, yet most significant stage of IIoT is integrating a strong cybersecurity framework. Security is an alarming concern of IIoT since the entire process depends on gathered data and uninterrupted network connectivity. Hence, if there are any vulnerabilities within the network or any sensors, the overall production process may encounter disturbance.
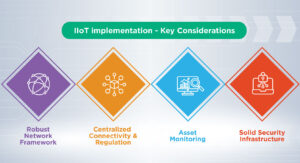
Organizations need to consider several components for effective and result-driven IIoT implementation. Let us discuss the major considerations:
- Robust Network Framework
IIoT leverages complex and advanced functionalities, ensuring the uninterrupted connectivity of every device, sensor, and application. For this purpose, a reliable and faster network framework is required. Therefore, organizations planning to incorporate scalable and effective IIoT need to invest in appropriate network equipment, such as routers and gateways. - Centralized Connectivity and Regulation
The industrial setup includes several devices, sensors, applications, and more, which the IIoT framework also needs to incorporate. To execute such incorporations successfully, a centralized approach is necessary in terms of connectivity. Centralized management and regulation of connectivity contribute to quick risk management and overall efficiency. - Asset Monitoring
The ability to track each asset is a crucial requirement of successful Industrial IoT integration. It allows organizations to appropriately use assets, maintain them skillfully, and sustain scalability. - Solid Security Infrastructure
Cybersecurity is a serious concern of effective IIoT integration. Therefore, while eliminating security issues, companies must consider establishing a strong security framework beforehand. Such an approach will enable the secure integration of IIoT.
Added Operational Efficiency
IIoT and its automation abilities can unlock remarkable operational efficiency, streamlining the overall production workflow. Furthermore, error identification and resolution are also effective in an automated production setting.
Enhanced Predictability
Industrial IoT leverages AI and ML to evaluate data, which offers better predictability abilities while executing a task. The process further forecasts when and how to use an asset, eliminating the requirement for long maintenance.
Higher Productivity and Lesser Human Error
While executing similar tasks again and again, the human brain may get tired and commit errors. However, IIoT empowers machines to operate automatically, while performing a task. Such an approach reduces the possibilities of human errors, boosting productivity significantly.
Reduced Cost and Sustained Worker Safety
IIoT infrastructure can assist organizations with their cost-saving endeavors. Such costs include workforce management, product defects, and others. Additionally, industrial areas and machinery are very complex and can threaten worker safety at times. An automated process eliminates such risks as well.
Security is one of the core risks of IIoT, apart from hardware issues. Organizations must predefine and take precautions against each risk for successful industrial IoT implementation.
Data Theft and Cyber-attacks
IIoT devices depend highly on data processing; the datasets include confidential information about the organization and how it operates. Attackers continuously try to break into the IIoT systems and network. If they successfully break into the system, the company may encounter devastating circumstances.
Hardware Malfunction
Disruption in hardware functionality is a huge concern of effective IIoT integration. If any device stops operating or faces disturbance to function appropriately, it can hinder the entire industrial process.
Alongside several operational benefits, IIoT also has several risks and threats, which can occur if the software or hardware malfunctions. To address such situations, it becomes necessary to set specific methodologies. In this regard, having a meticulous IT framework can be remarkably beneficial. An IT process can offer the following opportunities:
Faster risk assessment
While having a strong IT process within IIoT infrastructure, companies will be able to assess common risks faster and fix them in an efficient way. Therefore, the IT process can address software and hardware malfunctions and reduce risks in all manufacturing activities.
Stronger security implementation
An IT framework also enables continuous network and sensor evaluation, which contributes to vulnerability detection. Early detection also allows quicker mitigation. Hence, the IT process also empowers IIoT systems with a solid security approach.
IIoT is transforming and, hence, being implemented in different sectors for their industrial processes. Manufacturing, energy management, healthcare, automotive, agriculture, and construction are among the front-running domains to integrate such an approach. Let us examine the top use cases of industrial IoT-
Manufacturing
IIoT enables real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing tasks while automating the entire process. Alongside that, it offers advanced predictive maintenance, which strengthens equipment usability and lifecycle.
With automation and error-free operation, IIoT can contribute to faster and more efficient manufacturing, fulfilling the changing market expectations.
Energy Management
IIoT has revolutionized the energy and utilities industry by streamlining the production of energy, its dispersion, and consumption. Here, the mechanisms of automation and smart sensors are not only utilized for production purposes but also integrated at the consumers’ end to monitor their energy consumption rate.
Healthcare
The healthcare sector is leveraging IIoT to transform operations in hospitals and improve patient monitoring. Smart sensors in healthcare are effectively beneficial for the early detection of diseases and make it easier to offer appropriate medication.
Agriculture
One of the remarkable IIoT implementations has been in agriculture, shifting farming practices from traditional methods to smart procedures. The mechanism addresses ongoing agricultural challenges such as assessing crop health as per the weather, optimizing water consumption, scheduling irrigation timelines, and others.
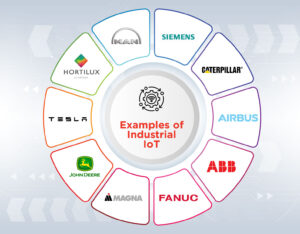
1. MAN
MAN is a Truck & Bus Company. The company provides its customers with a tracker that spots engine faults or other potential failures. Hence, it saves customers time and money.
2. Siemens
Siemens is a German multinational conglomerate company. The company wanted to build fully automated, Internet-based smart factories. The company builds automated machines for brands like BMW.Siemens introduced an operating system called Mindsphere, the cloud-based IoT unit from Siemens, which basically aggregates the data from all the different vital components of a factory and then processes them through rich analytics to produce useful results.
3. Caterpillar (CAT)
It is an American machinery and equipment firm. The company uses augmented reality (AR) applications to operate machines from fuel levels to when air filters need replacing. The company sends basic instructions on how to replace it via an AR app.CAT began its industrial machinery with intelligent sensors and network capabilities, which allow users to optimize and monitor processes closely.Caterpillar has brought about 45% efficiency into its production by putting IoT technology to use. Tom Bucklar, the IoT and Channel Solutions Director of Caterpillar, said that customer satisfaction is at the forefront of their efforts.
Caterpillar, in order to deliver real-time information to all the dealers regarding their equipment, joined hands with AT&T’s IoT services in early 2018. With the help of AT&T, they had widespread connectivity of resources.
4. Airbus
It is a European multinational aerospace corporation. The company had launched a digital manufacturing initiative known as Factory of the Future to streamline operations and increase production capacity.The employees use a tablet or smart glasses (designed to reduce errors and bolster safety in the workplace) and smart devices to assess a task and communicate with the main infrastructure or locally with operators and then send that information to a robotic tool that completes it.
5. ABB
ABB is a Swiss-Swedish multinational corporation that is basically involved in the production of robots. It uses connected, low-cost sensors to monitor and control the maintenance of its robots to prompt repairs before the parts break.The company is using connected oil and gas production to solve hindrances at the plant, thereby achieving business goals in a cost-effective way. The company had developed a compact sensor that is attached to the frame of low-voltage induction motors, where no writing is needed.By using these sensors, the company gets information about motor health via smartphones or on the internet through a secure server.
6. Fanuc
Fanuc is one of the largest suppliers of industrial automation equipment in the world. The company developed the FIELD System (Fanuc Intelligent Edge Link & Drive System), an open platform that enables the execution of various IIoT applications that focus on heavy devices like robots, sensors, and machine tools.Alongside cloud-based analytics, Fanuc is utilizing sensors inside its robotics to anticipate any failure in the mechanism. With the help of this, the supervisors are able to keep up with the schedule and reduce costs.
7. Magna Steyr
It is an Austrian automotive manufacturer that offers production flexibility by using the concept of smart factories.The factory network system is digitally equipped. It is also using Bluetooth to test the concept of smart packaging and help the employees to better track the assets and efficiency between operations.
8. John Deere
It is an American corporation that manufactures agricultural, forestry, and construction machinery. The company bought the self-driving vehicle revolution, which no other company had done.
John Deere was the first company that coined the concept of GPS in tractors. The company has deployed telematics technology for predictive maintenance applications.
9. Tesla
It is an American automotive and Energy firm specializing in the manufacturing of electric vehicles. The company is leveraging IT-driven data to move their business forward. They improve the functionality of the products via software updates.Autonomous Indoor Vehicles by Tesla have changed the way the batteries were consumed previously. These batteries were chargeable on their own without any interruption.Tesla also introduced a feature that helped customers to control and check their devices from anywhere through their smartphones.
10. Hortilux
The company provides lighting solutions. They introduced Hortisense, a digital solution that safeguards various operations.
It uses smart sensors operated through the cloud to monitor the light levels and efficiency of the offered light. This information can be monitored and checked from anywhere on any device.
Contemplating the Future of IoT Devices!
Industrial IoT is indeed a revolutionary advancement for different sectors that contributes to enhanced productivity, efficiency, and quality. Such devices enable automation, adding more flexibility to industrial activities.
In 2022, the global industrial IoT market exceeded $544 billion, which is anticipated to surpass $3.3 trillion by 2030. These numbers are enough to highlight how IIoT is progressing. The evolution of notable technologies shall also be significant for the enhanced implementation of IoT devices. The 6G network is the upcoming connectivity milestone that can transform the performance of IoT systems.
However, security concerns will still be a great challenge for such an approach. While addressing such difficulties, adopting blockchain technology can be extremely advantageous. Additionally, continuous advancements in AI, ML, and edge computing will also play a vital role in the future implementation of IIoT infrastructure. Whether it is a small business, end-user, or large-scale business, all the segments will have equal benefits when integrating an automated industrial process.
Was the blog informative? If so, you’ll like to explore our other insightful content as well!
You May Also Like to Read-