How often do we use chatbots and generative AI, sharing our personal information, and don’t think about the consequences? The consequences can lead to privacy violations, information misuse, and even worse- financial scams and reputational damage.
Studies indicate that one of the AI bot data breaches, which occurred in February 2025, exposed the personal information of over 30,000 users. The number can go beyond imagination if the user base is larger. For example, ChatGPT is a platform with over 800 users per week. So, in any case of data breach against ChatGPT, a larger number of people’s personal data will be at stake.
Recently, over 4,500 ChatGPT conversations got indexed for search engines. People were just a few clicks away from locating others’ names, phone numbers, locations, and even details on their bank balance. Although the feature was later disabled, it was an alarming incident highlighting the dangers that AI bots can pose to individuals.
Let us understand how sharing personal information with generative AI bots can put us into danger and how to stay safe.
Understanding User Privacy in the AI Era:
AI has doubtlessly simplified several critical tasks, for which the global public is adopting it very quickly. Considering user privacy is the last aspect people often overlook when addressing their tasks with AI bots. However, technology has always been a two-edged sword with benefits as well as drawbacks. AI, in this regard, has assisted us in simplifying critical tasks, but with greater privacy concerns.
Whenever we use AI, we share prompts possessing a certain amount of information. Unaware of the fact that data can be repurposed, we often end up sharing sensitive information about ourselves. Apart from that, we use AI bots to address diverse challenges, including finance, healthcare, employment concerns, and even very personal issues. Every insight shared becomes data, which can be exploited for training AI models, creating targeted ads, and even more dangerous purposes.
For example, when we seek financial advice from AI bots sharing our bank balance, the data can be misused for model training and create targeted ads. Alongside that, user privacy will also be compromised if the data gets stolen. Below are the major privacy concerns while using AI tools-
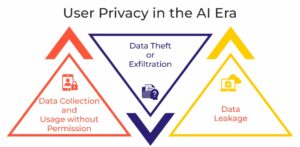
- Data Collection and Usage without Permission:
Primary concern arises when the audience remains unaware of where their data has been utilized. AI model often collects user data without consent, which leads to significant privacy risks. Furthermore, AI models also use collected data, which may or may not include sensitive information, without permission for repurposing.
- Data Theft or Exfiltration:
The data stored by AI applications is also prone to theft. Cyber attackers often employ strategies like prompt injection attacks to manipulate AI systems and expose user data. For example, suppose a user processes a prompt by uploading a confidential document. In that case, hackers can use manipulative prompts on a genAI model to identify and share such documents, which later can be exploited negatively.
- Data Leakage:
Another privacy concern takes place when AI systems encounter security weaknesses or become vulnerable, exposing user data to malicious sources. Data leakage can be an outcome of intentional or unintentional data exposure. For example, if a financial institution uses an AI application to handle its customers, it uploads customer details to the app.
A network vulnerability caused by an unintentional technical glitch or intentional exposure can lead to major data leakage and privacy breaches.
So, user privacy in the AI era is a delicate thread that can be easily snapped, putting sensitive user data at risk.
How do Chatbots and LLMs use user Data?
Have you ever wondered how AI bots and applications are able to generate human-like responses?
AI models are trained and fine-tuned on a vast amount of historical and real-time datasets. Notably, data becomes outdated very quickly, as audience needs change at a rapid pace. So, collecting historical data becomes easier for AI developers, but how to collect ongoing data?
User interaction has been a great source for training data collection apart from feedback and observational data. For example, the conversations users generally have with ChatGPT and other genAI bots are stored and utilized to train and improve the models.
Very rarely, such AI applications seek consent from users before leveraging their personal interactions as training data. Shockingly, a large number of users have a limited idea about how their personal information is being used to train LLMs and AI chatbots. As a result, they share sensitive information in a casual way and increase the possibility of encountering a data breach.
AI models generally use user data for the following purposes:
- Model training and improvement.
- Boost performance and accuracy.
- Integrate personalization and tailored recommendations.
- Enhance contextual awareness and overall functionality.
AI Trends and the Privacy Fears:
We often see emerging AI trends capturing attention worldwide. Recent trends include Ghibli-style image generation, AI-music composition, and 3D video generation. Observing the popularity, individuals often follow these trends, processing their personal photos, voice notes, and videos. Nevertheless, following these trends can also impose remarkable privacy risks.
Let’s understand how these trends increase privacy risks:
- Data collection and retention:
As discussed earlier, AI models are fine-tuned on user data. Hence, uploading photos, videos, and voice clips allows AI applications to collect, store, and assess personal data of the users. Unexpectedly, there is less clarity on how long the datasets will be stored and used.
- Biometric data at Stake:
Photos and videos include facial and voice data consisting of biometric information of individuals. Hence, sharing such files will certainly expose your biometric data, which can be used without consent.
- Third-party Sharing and Identity Theft:
Many AI applications share user data with third parties. Sharing personal data, such as a photo, can lead to identity theft by third parties. Creation and circulation of deepfakes become easier under such situations.
- Metadata Exposure:
Photos, videos, and voice notes include metadata like location and device name, which is also considered personal information. So, following such AI trends can also expose your metadata.
ChatGPT Conversations were on Search!
One of the major user data exposures took place recently when thousands of ChatGPT conversations were found ranking on the search engines. Although ChatGPT’s developing firm, OpenAI, has always advocated prioritizing user privacy. Following the revelation of users’ personal chats, the company faced backlash for raising privacy risks across ChatGPT’s global user base.
Reportedly, over 4,500 ChatGPT conversations got indexed on the search. Even if someone deleted their chat, it was still visible in the search. After facing criticism, OpenAI disabled the feature by calling it a ‘short-lived experiment’. However, it took significant time to remove the chats that were already being indexed.
ChatGPT backed the incident by highlighting the goal of strengthening ChatGPT’s reach with publicly shared knowledge. Nevertheless, the AI leader considered the threat of accidental exposure of personal and sensitive data over the possible opportunities while disabling the feature. The incident has raised major privacy concerns among the user base of ChatGPT and other AI chatbots.
Notably, ChatGPT conversations are saved until and unless users manually delete them. Even after deletion of the chats, they are stored in the OpenAI systems for another 30 days before getting permanently removed. Moreover, ChatGPT retains anonymous chats or chats without login for a significant time. So, users have limited transparency on how AI models are using their data.
Whether it was an intentional strategy or an unintentional step, the chat indexability of ChatGPT is doubtlessly a warning on how user privacy is becoming more unsafe day by day.
And more…
There are other examples as well where AI systems and genAI solution providers were found putting user data privacy in danger. Let’s discuss a few-
Microsoft’s Accidental Data Leak:
In 2023, the Microsoft AI research team accidentally exposed 38TB of private data of users and employees. The datasets included passwords, confidential credentials, and more than 30,000 Microsoft Teams conversations.
The incident raised questions about Microsoft’s data security and privacy measures.
Slack AI Data Exfiltration:
In August 2024, a report by PromptArmor showed data privacy concerns related to Slack AI after identifying possible data leakage through prompt injection. The tool is used remarkably for conversation summarization and finding answers. The incident of data exfiltration through prompt injection raised the privacy risk among individuals and companies that used the tool for organizational purposes.
WotNot PII Leak:
The AI startup, WotNot, was found to create a notable privacy threat by exposing personally identifiable information (PII) of individuals, including data about passports, employment details, medical records, and more. Such an amount of data can be misused by cybercriminals, leading to further devastating situations.
Legal and Regulatory Guidelines to Sustain User Privacy:
Indeed, policymakers and governments in various regions have consistently taken initiatives to address the risks associated with technological advancements, including AI. There are set regulatory benchmarks for data privacy across the world that prevent misuse or unlawful use of user data by tech providers. Let’s assess the leading guidelines for better understanding-
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) of the European Union:
GDPR offers a thorough guideline on how companies ethically handle and use the personal data of users. Under this regulation, companies must maintain transparency with the users while collecting, storing, and using their data. Moreover, this allows firms to store user data for a specific period of time only, deleting the same after fulfilling the key purpose of collecting data.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States:
CCPA empowers the users of California to manage their personal information while sharing it with third parties. According to this data privacy guideline, users have the right to know how and where their data is being used, the right to delete their personal data stored by any business, the right to opt out the usage and sale of their personal data by third parties, alongside the right to put limitations to use or disclose their personal data.
China’s Interim Measures:
China’s Interim Measures for the Administration of Generative AI Services, introduced in 2023, propose advanced AI regulations. As per this guideline, generative AI solutions must acknowledge and protect the rights and priorities of others, safeguarding the physical and mental health of others. They must not violate the privacy rights, personal information rights, privacy rights, reputation rights, honor rights, and portrait rights of others.
EU Artificial Intelligence (AI) Act:
The EU AI Act specifically focuses on AI privacy, sustaining governance, transparency, and risk management while using artificial intelligence. It prohibits AI systems from untargeted scraping of facial images from the internet, alongside real-time remote biometric identification.
Furthermore, it rules high-risk AI practices to adhere to resilient governance guidelines and maintain high-quality test data.
How to Stay Safe and Protect User Privacy?
The best way to utilize innovations like AI and safeguard user privacy is to leverage them as tools while human users remain in control. Hence, users must have a clearer idea of how AI models are using their data. For this purpose, AI developers, organizations, users, and the government all have significant roles to play. Following are the best practices to stay safe in the AI era-
For Individuals or Users:
Users must be mindful while sharing personal details with generative AI models or any other digital channels. Sharing limited information and staying safe is the best practice one can adopt in the AI era. Furthermore, seek transparency from service providers regarding how they utilize user data and whether they sell your data to third parties.
Hence, staying cautious while sharing sensitive data is important. Knowing where your information is being stored and for what purpose is a crucial step.
For AI Developers:
While aiming for a secure future, AI developers must prioritize developing responsible and ethical AI models. This will definitely lead to lawful AI practices, meeting the ethical standards. Such an approach will further help develop reliable, trustworthy, and beneficial AI model development.
Additionally, AI development firms should also maintain transparency with their user base so that users have a clearer picture of how their personal data is being used.
For Organizations:
Organizations that use AI models for operational benefits must implement an advanced governance framework. Moreover, they should prioritize ethical AI use, focusing on data privacy above all else. Data masking and pseudonymization can be an effective strategy in this regard. Organizing training sessions for employees on the ethical use of AI within the firm will allow people to know what to share with AI agents while sustaining data privacy.
For Government and Policymakers:
Since AI models are advancing notably, there is a need to formulate sophisticated data privacy laws. Therefore, the government and policymakers must consider the growing data security concerns and implement more robust policies that safeguard user data.
Is Privacy a Myth or a Far-fetched Dream?
Although AI leaders promise not to misuse user data and claim to implement advanced strategies to safeguard it, they still train their models using user data. So, is user privacy real or just a myth in the AI era?
The appropriate answer to this question is vague and warrants further discussion. Whatever we share with AI bots is somehow being exploited, whether by cyber attackers or AI firms. Hence, it is crucial to stay cautious and alert when sharing information with such AI bots.
Because the information you share with AI bots becomes their training data in no time, alongside that, data breaches against these AI models can also create a threat to user data privacy, leading to stolen and misused information. Issues like AI hallucination, bias, and misleading remarks of AI models also exist, which make using these technologies further dangerous.
Nevertheless, AI models will continue to evolve and upgrade. The need of the hour is robust privacy policies and appropriate compliance. ChatGPT has also launched GPT-5 for all users. It will be interesting to see how effectively the company sustains user privacy alongside making improvements to its AI models.
Stay current with the ongoing digital transformation and learn the strategies to protect your data in the tech-driven age with HiTechNectar!
FAQs:
1. Can ChatGPT developers see my chats?
Ans. Conversations on ChatGPT or other genAI bots are usually treated as data to train future models. So, there is a high possibility that human trainers and developers may closely observe and scrutinize chats on these AI models.
2. What to never tell ChatGPT?
Ans. Refrain from sharing personal information with AI bots like ChatGPT, such as your name, phone numbers, email addresses, financial details, passwords, credentials, medical history, excessively personal details, and others.
3. How does the use of AI raise concerns about privacy?
Ans. While using AI, we share our personal information and data. This information can be repurposed to train AI models, which is a serious privacy concern triggered by AI.https://hitechnectar.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/hitech2white-min-1.png
4. How do privacy concerns manifest in AI systems?
Ans. User data collected by AI bots can be exploited in various ways, including repurposing for AI model training and personalized advertising. If the data is stolen, it can be used for malicious purposes, such as scams.
Recommended For You:
DeepSeek AI vs ChatGPT – Which AI is Better for You?
ChatGPT Shopping: How to Optimize Your E-commerce Store for AI Search Rankings?


