Many organizations today are shifting to remote work culture, resulting in an increased demand for VPN.
Not only does it help navigate the world wide web seamlessly, but it also provides the required security to keep data safe. This is an imperative requirement for enterprises globally.
There are various VPN protocols in the market that we can choose from. OpenVPN has been at the top of the list till late.
It had established its top rank in terms of security and performance over other VPN protocols.
However, WireGuard became the new favorite since its launch in 2018.
What is that X factor which makes WireGuard a worthy alternative to OpenVPN? Let’s go through the comparison of both the protocols to understand more.
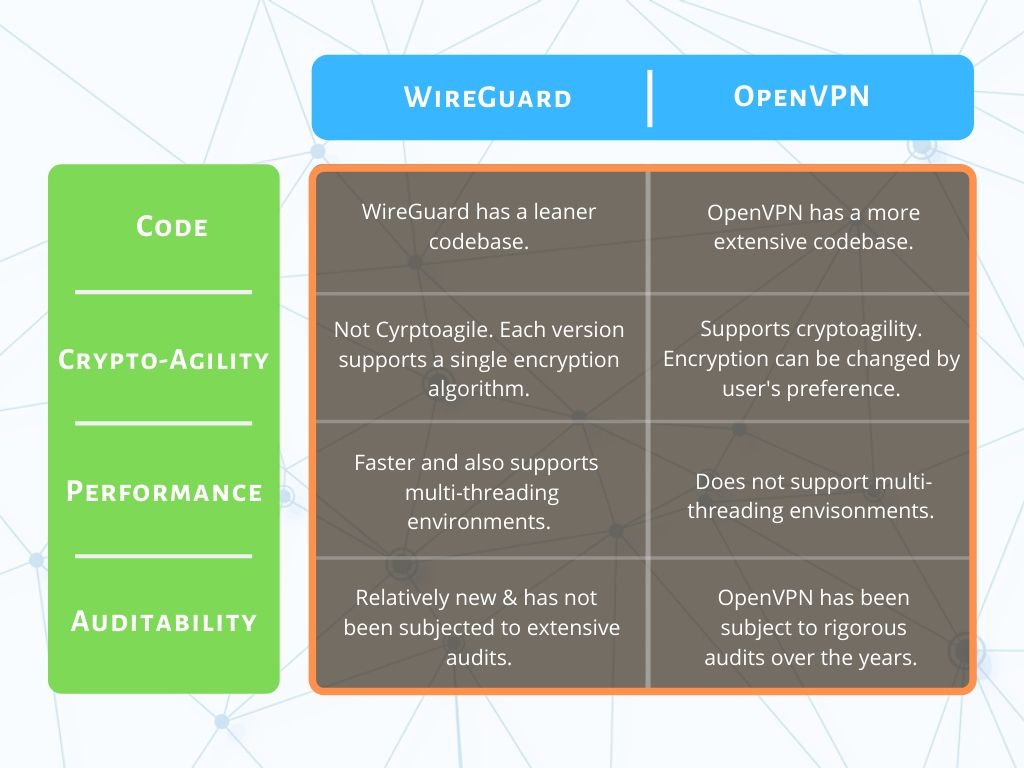
WireGuard vs. OpenVPN: A Quick Comparison
With about 4,000 lines of code as against 70,000+ of OpenVPN, WireGuard provides better security, erstwhile making it more agile and efficient.
With memory being a premium these days, any program that consists of a smaller fingerprint deserves a thumbs up!
The lesser lines of codes in WireGuard makes it easier for developers to address any vulnerabilities in the system.
Less code also means lesser bugs. It also provides attackers with a small surface to attack, reducing the chances of a man-in-the-middle attack.
Crypto-agility is the ability of a system to shift to alternative cryptographic algorithms. This can be achieved without having to make any changes to the existing system in place.
OpenVPN is crypto-agile, whereas WireGuard is not.
Encryption for OpenVPN can be changed or modified according to the user’s preferences. Security certificates are required for their implementation. So, we can say that OpenVPN is a certificate-based protocol.
WireGuard uses a system called “Versioning.” It creates or releases a better or improved version of their product in versions. So, updating WireGuard is simpler.
Not being crypto-agile makes WireGuard less complicated and hence more secure. This leaves WireGuard with lesser vulnerabilities.
Regular updates of OpenVPN are more complex and time-consuming. A new set of keys and key lengths are required to be set in place on a one-on-one basis.
WireGuard is easier to install and configure as compared to OpenVPN. It is also easier to setup.
OpenVPN is built with complex code. Modifying the code to update the system is a tedious and time-consuming process.
WireGuard provides easy cross-platform compatibility and usability owing to its compact codebase.
Even though it is an established protocol, OpenVPN is not the best protocol when it comes to performance.
OpenVPN is unable to stand up to the expectations when it comes to multi-threading environments.
WireGuard is integrated into the kernel space. This makes it faster using the multi-threading abilities of CPUs more efficiently. WireGuard performs better than OpenVPN when it comes to throughput and ping times.
OpenVPN is a veteran in the technology industry. It has been audited by programmers time and again.
It has earned the trust of programmers with the extent of audits it has undergone over time. Being open-source has made the protocol easier to audit.
WireGuard, on the other hand, is comparatively new. It hasn’t been put through rigorous audits. Considering its code length, it is easier to audit than OpenVPN.
With time, it will prove its mettle and is sure to give OpenVPN a run for its money.
Tabular Comparison of WireGuard and OpenVPN
Conclusion
With so many VPN options in the market currently, it can be quite tedious to hunt for that perfect VPN, which suits your business the best.
For the time being, OpenVPN and WireGuard have proven to the market that they stand out among the crowd and are worthy competitors.
The above comparison is proof that there is quite less that differentiates the two to provide us with a clear winner.
All-in-all, if you are to choose one, if you are not much into lighter programs and then OpenVPN is the one to opt for.
On the other hand, if you are looking for a lighter, simpler VPN, it is recommended to opt for WireGuard. Many organizations use two VPNs at times, so you could also give both of them a chance to identify which is a better match for your organization.
You May Also Like to Read:
Hyperconverged Infrastructure vs. Cloud: What’s the Difference?