The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing technology interactions by merging the physical and digital worlds. Nowadays, smart homes automatically manage lighting and temperature settings, and even industrial machines can forecast when maintenance will be required. It is truly boosting the quality of life and improving business operations.
This technology makes it possible for devices to gather, analyze, and share information autonomously by integrating sensors and software into regular items. Such a mesh of interconnected devices increases productivity and offers new opportunities in various spheres, including health care, agriculture, transportation, and manufacturing.
What is IoT? What are the technologies behind this enormous framework of interconnected devices, and how does it operate? This blog will elaborate on the major elements of the Internet of Things. Besides, we will look into the different areas in which it is affecting the world and consider its positive impact.
What Is IoT?
To understand what is IoT, let’s start with the basics. The Internet of Things involves a collection of devices that communicate with one another and with computers over the Internet. It includes sensors, software, network connectivity, and other items in your home such as air conditioners and even commercial machines.
Because of communication between devices, there is progress in efficiency, a reduced need for human effort, and streamlining of threads in many industries. Once the devices are connected to the internet, the entire framework of how we interact with the world and technology changes.
So, what is IoT’s ultimate goal? It’s about creating a smarter, more efficient world. Data says that the number of IoT devices is about to double in the world by 2030, from 15.9 billion in 2023 to more than 32.1 billion.
What Are the Key Technologies Behind IoT?
Now that we’ve answered, “What is IoT,” let’s dive into how it works.
The driving force behind the expansion of this technology is the growth in internet accessibility, sensor technological advancement, and computing power. Smart technology was limited at first because chips were expensive and large. Today, cost-effective, efficient, and compact components make embedding intelligence into everyday objects practical and easy.
Nowadays, virtually any application can be supported, even by low-powered microcontrollers with low memory storage. This has made embedding smart technologies into consumer products, industrial tools, and even urban infrastructure much easier. As a result, technology-driven automation and optimization-led “smart” homes, factories, cities, and even agricultural systems emerged.
Three technologies are critical enablers of the Internet of Things:
Sensors and Actuators – Sensors help capture real-world data, including temperature, humidity, motion, pressure, and so forth. Actuators, on the other hand, allow devices to activate specific results based on the data collected. With these tools, devices can perform tasks autonomously, resulting in real-time automation and monitoring.
Connectivity and Communication Protocols – Smart devices use numerous wireless and cable-based communication technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 5G, LoRaWAN, and ZigBee to share data with other devices or the cloud. These types of protocols enable data to be exchanged without barriers and help monitor and control devices from a distance.
Cloud Computing and Edge Computing – By virtue of cloud platforms, storing and processing power is available on demand, which helps in the management of data collected from various smart devices. This data is processed at the edge of the network in edge computing, which shortens latency and enhances real-time decision-making, especially in time-sensitive uses, such as healthcare and industrial automation.
Applications of IoT in Diverse Industries
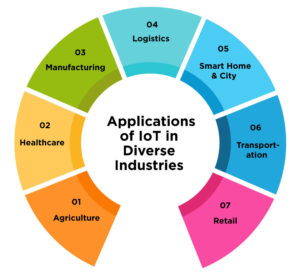
What is IoT’s impact on our daily lives? It impacts an extensive range of industries and augments functions, decision-making, and user experience.
In agriculture, systems and sensors can be connected to track soil moisture and weather data, allowing for irrigated crops to thrive. In healthcare and medicine, wearable devices can monitor health vitals in real time, allowing for early identification of a health problem.
Manufacturing plants have embedded systems to monitor machinery, predict maintenance requirements, and cut down on downtime. The logistics industry is using smart tracking systems for effective inventory control and supply chain management.
It also enhances smart city development through advanced traffic control, energy-efficient buildings, and real-time information for public transportation. With smart home appliances, thermostats, and security systems, it makes home life even more pleasurable and manageable.
It is also reforming transportation by enabling smart traffic management, vehicle tracking, and predictive maintenance for fleets. In the retail industry, networked devices enhance inventory management, personalized shopping experiences, and supply chain optimization through real-time data analytics.
The Future of IoT: How It’s Changing the World
What is IoT’s future? This new technology is paving the way for a smarter and more sustainable world fueled by innovations that boost efficiency and minimize waste. Companies are embracing circular economy models, leveraging technology for predictive maintenance, and extending product lifespans.
However, the rise in connected devices also heightens the demand for enhanced security. As this technology continues to grow, businesses must focus on security and data privacy to address consumer concerns, fostering trust and ensuring safe interactions with these devices.
Another significant trend is the integration of artificial intelligence, which allows devices to make informed decisions based on data and improve their functionality. By merging AI with smart systems, industries can enhance predictive maintenance and optimize operations, such as making real-time health adjustments in medical devices.
Simultaneously, the shift from centralized cloud platforms to decentralized systems, like blockchain, is improving security and reducing dependence on the cloud. As these technologies advance, the Internet of Things will keep transforming industries while also presenting new challenges related to security and data management.
But what is IoT’s biggest hurdle? As the Internet of Things becomes more widespread, issues like data security, privacy concerns, and interoperability among various devices need to be tackled. The risk of cybersecurity threats grows with the increasing number of connected devices, making strong security measures vital.
Looking Ahead!
Achieving standardization across ecosystems is essential for smooth integration and communication between IoT devices. Despite the above-mentioned hurdles, the future of IoT looks bright, with ongoing innovations set to further enhance automation, efficiency, and connectivity in our ever-evolving digital landscape.
Dive into the realm of IoT and emerging technologies through our detailed blogs. We take a thorough approach to content creation, ensuring our readers receive valuable insights.
You May Also Like to Read:
IoT Solutions for the Automotive Industry
IoT and Augmented Reality Examples: Promising Connections


