Software development has come a long way from manual management and deployment to a fully automated process. Containerization, in this regard, streamlines the software development process by containerizing all the code, files, and libraries for a particular application that requires running on any infrastructure.
Studies find that over 70% of developers worldwide are using container orchestration solutions to integrate a fully managed development approach. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leading provider of container orchestration solutions with Elastic Container Service (ECS) and Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS). Nevertheless, both solutions differ significantly.
In this blog, we’ll differentiate between ECS vs. EKS to understand when to choose what will be beneficial for your business. First, let’s thoroughly understand container orchestration.
What is Container Orchestration?
Container orchestration is an advanced process to automate the management, deployment, scaling, and networking of containerized applications throughout their lifecycle. It makes it convenient to deploy software in multiple environments, sustaining scalability.
Such an approach allows developers to develop software faster, save costs, and integrate security. Container orchestration can be used for multiple purposes, including software provisioning, deployment, configuration, resource allocation, monitoring container health, load balancing, and more. Enterprises generally integrate this process since they need to deploy and manage numerous containers and hosts.
Notably, in 2024, the global container orchestration market was valued at $1.7 billion. The industry is set to grow with a valuation of $8.5 billion by 2030. The key reasons for such growth are the increased adoption of containerized applications and microservices architecture.
What is Elastic Container Service (ECS)?
Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) is AWS’s own, fully managed container orchestration service that helps developers run, scale, and manage Docker containers without wrestling with the underlying control plane. It is tightly integrated with AWS tooling and offers both EC2-based and serverless launch options, so teams can pick up the level of infrastructure control they want.
The key features of ECS are simplicity, quick setup, AWS integration, and task definition.
What is Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)?
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) is a managed Kubernetes offering within AWS. It provides developers with a production-ready Kubernetes control plane on AWS. So, developers can run standard Kubernetes workloads and use the broad Kubernetes ecosystem, including Helm charts, Operators, service meshes, and more.
All these capabilities are possible with AWS handling the control-plane availability and scaling. EKS also empowers managed node groups and can run pods on Fargate, a serverless computing engine by AWS. Compatibility in Kubernetes, flexibility, extensibility, and a managed control plane are the key features of EKS.
Differentiating ECS vs. EKS
Though both ECS vs. EKS help in running containers, they have different approaches, features, and compatibility levels. Let us discuss the major differences-
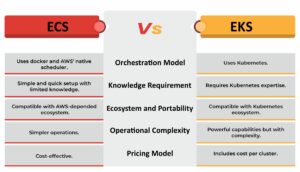
Orchestration Model
ECS uses AWS’s native scheduler. On the other hand, EKS runs upstream Kubernetes. That means EKS supports the full Kubernetes API and ecosystem, while ECS focuses on simple AWS-native workflows.
Knowledge Requirement
ECS is simpler and faster to adopt for teams already in AWS. Conversely, EKS requires Kubernetes knowledge but gives more flexibility to teams that need it.
Ecosystem and Portability
EKS workloads are portable across clouds or on-premises infrastructures. But ECS is more AWS-centric, which can support workloads, highly depended on AWS cloud. Such a method is convenient for seamless integration but with limited portability.
Operational Complexity
ECS makes the container management operations simpler while handling complex tasks automatically. Conversely, EKS offers powerful capabilities which come with complexity. It gives developers control but requires them to assume Kubernetes operational responsibilities unless they use managed node groups or Fargate.
Pricing Model
ECS is cost-effective while EKS can charge cost per cluster. EKS has an additional control-plane fee that can be applied across multiple clusters. Conversely, ECS does not charge a per-cluster control-plane fee. So, costs are primarily for computing power and storage.
Features
EKS supports advanced patterns, such as DaemonSets, CRDs, Operators, and complex network policies. In contrast, ECS covers most common service patterns but lacks some advanced Kubernetes-native constructs.
ECS vs. EKS: When to Use Which Service?
Both AWS ECS and EKS are advanced container orchestration solutions. However, developers must choose a solution according to their needs and skillsets. Apart from that, a hybrid approach can also be beneficial in specific instances.
Developers must use AWS ECS while prioritizing simplicity and quick setup in the container orchestration process. Managing applications built on a microservices architecture is easier while using ECS. In addition, choosing ECS will be beneficial when your infrastructure relies heavily on AWS services.
Similarly, using AWS EKS will be convenient when a team of developers has expertise in Kubernetes. Additionally, choosing EKS will be advantageous while looking for advanced customization, ecosystem compatibility, portability, and enterprise-level features.
Developers can also embrace a hybrid approach, combining ECS and EKS. For this purpose, use ECS where simplicity and cost matter, and EKS where advanced orchestration or portability is critical. It is worth noting that AWS tools work well across both services. If you are looking for a simplified yet customizable approach to scaling containerized applications in the AWS cloud, you can choose a hybrid approach.
Concluding Remarks!
ECS gives a strong, AWS-native path to containers. But EKS offers developers with all the capabilities of Kubernetes and its ecosystem. Nevertheless, it is critical to ensure that the service developers choose compatible with their team’s skills, portability needs, operational appetite, and budget.
Read our in-depth blogs and discover the emerging technologies that can be beneficial for your business.
FAQs:
Q1. Which is cheaper, ECS or EKS?
Answer: ECS is less expensive than EKS.
Q2. Why choose Kubernetes over ECS?
Answer: ECS is available only on AWS and can only run Amazon’s cloud services. On the other hand, developers can deploy Kubernetes on any infrastructure they want.
Recommended For You: