As an IT industry professional, you must have encountered two terms frequently.
Hypervisors and Dockers are currently two of the most used software in the industry. This is due to the surge in the use of virtual machines and applications.
Hypervisors and Dockers are not the same, and neither can be used interchangeably. People are often confused between the two because of their applications related to virtualization.
Let us explore the differences between hypervisor and Docker so that you can figure out as to which suits you the best.
The most significant difference between hypervisors and Dockers is the way they boot up and consume resources.
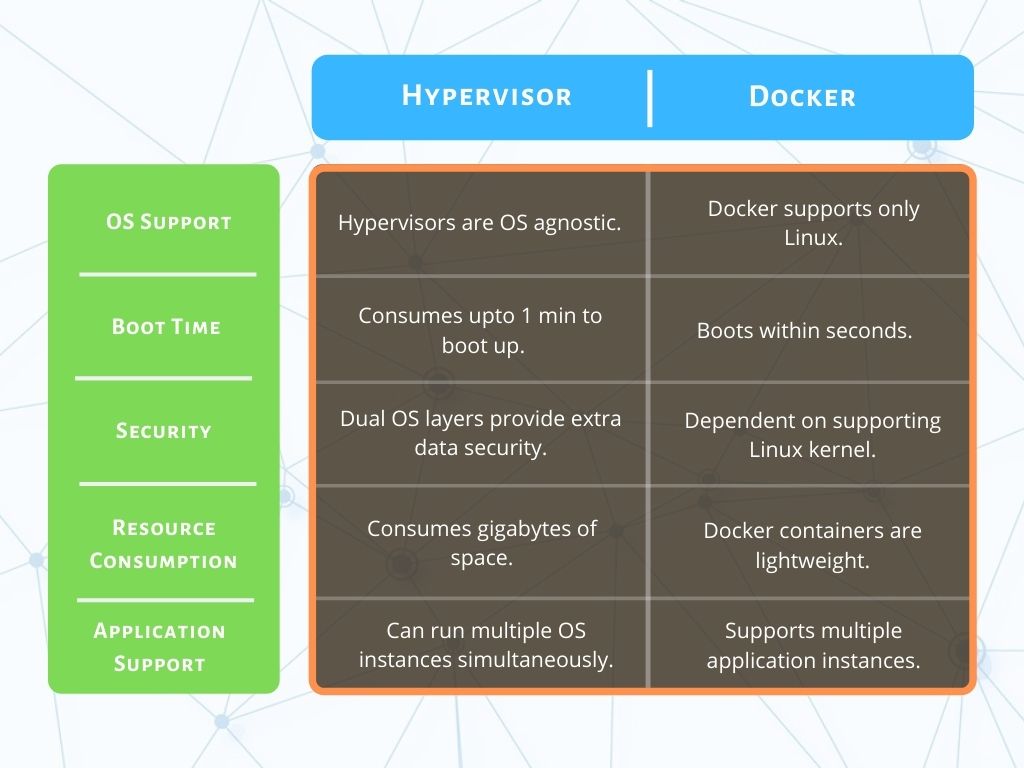
Hypervisors are of two types – the bare metal works directly on the hardware while type two hypervisor works on top of the operating system.
Docker, on the other hand, works on the host kernel itself. Hence, it does not allow the user to create multiple instances of operating systems.
Instead, they create containers that act as virtual application environments for the user to work on.
A hypervisor allows the users to generate multiple instances of complete operating systems.
Dockers can run multiple applications or multiple instances of a single application. It does this with containers.
Hypervisors enable users to run multiple instances of complete operating systems. This makes them resource hungry.
They need dedicated resources for any particular instance among the shared hardware which the hypervisor allocates during boot.
Dockers, however, do not have any such requirements. One can create as many containers as needed.
Based on the application requirement and availability of processing power, the Docker provides it to the containers.
Also Read: Kubernetes and Docker: Either or Both?
As Dockers do not require such resource allocations for creating containers, they can be created quickly to get started.
One of the primary reasons why the use of Dockers and containers is gaining traction is their capability to get started in seconds.
A hypervisor might consume up to a minute to boot the OS and get up and running.
Docker can create containers in seconds, and users can get started in no time.
If we consider both hypervisor and Docker’s architecture, we can notice that the Docker engine sits right on top of the host OS.
It only creates instances of the application and libraries.
Hypervisor though, has the host OS and then also has the guest OS further. This creates two layers of the OS that are running on the hardware.
If you are to run a portable program and want to run multiple instances of it, then containers are the best way to go. Hence you can benefit significantly with a Docker.
Dockers help with the agile way of working. Within each container, different sections of the program can be developed and tested.
In the end, all containers can be combined into a single program. Hypervisors do not provide such capability.
Security
Hypervisors are much more secure since the additional layer helps keep data safe.
One of the major differences between the two is the capability to run operating systems or rather run on operating systems.
Hypervisors are OS agnostic. They can run across Windows, Mac, and Linux.
Dockers, on the other hand, are limited to Linux only. That, however, is not a deterrent for Dockers since Linux is a strong eco-system. Many major players are entering into the Dockers’ fray.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
It is true that Dockers and hypervisors are majorly different, even though they might seem similar to the layman.
They both serve different segments of the IT world based on the applications.
It is up to the organization to choose which one to opt for based on what suits them the best.
Dockers help run multiple instances of the same application, whereas hypervisors with the VMs help run multiple instances of multiple applications.
The capability to run an entire OS does come handy. Often, organizations opt for both and leverage the advantages of both hypervisors and Dockers to extract the highest level of productivity possible.
You May Also Like to Read:
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Hypervisors?



 Conclusion
Conclusion