It is not news that data storage security is a sensitive matter for every organization. Still, we have observed that most businesses do not have efficient, modern technologies to back up their database.
For any business, big or small, data loss is a significant headache and could seriously hamper any development. To deal with it, you need to understand that several reasons could lead to data loss:
- Malware and viruses.
- Malicious insiders.
- Power outages.
- Corrupt files.
- Involuntarily deleted, formatted and lost data.
- Accidental damages.
It is crucial to ensure data security on every mode and from it on-premises, VM storage, SQL server, remote access, or over the cloud.
Multiple measures can be taken to stay up to date with modern technologies, and backup and snapshots are two of them.
Also Read: Encryption as a Service Explained in Detail
Both snapshots and backup aim to help you in data loss situations by creating a copy of your data. But their processes are notably distinctive from each other.
These differences need to be carefully acknowledged while making any storage recovery decisions.
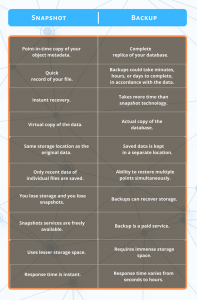
Snapshot vs. Backup: Understanding the Two Concepts
Snapshot is essentially a quick record of your system metadata at a given moment, retained in a unit storage like SAN or NAS.
The record could be an image, volume, or database file of any type. It allows you to recover data from a former state if required.
Thus, the snapshot is a point in time recovery solution. It is a significant mitigating point in adverse circumstances like user or hardware failure, data corruption, or power outage.
The snapshots are saved in a similar storage system, making themselves vulnerable to high-level storage or data loss.
Snapshots overview:
- Point-in-time.
- Compact.
- Similar Storage location.
- Metadata recording.
- Overlapping capabilities.
- Time-sensitive.
A Backup is a complete standalone replica of your database, including mailbox, application packages, images, and videos that are stored away in a separate system.
Backups, unlike the snapshots, can handle the recovery of an entire set of files and applications.
A sound backup system can re-enact other sophisticated structures like active directory, database server, and computer clusters.
Backups comprise multiple techniques, such as snapshots, encryption, data deduplication, and backup destination flexibility, to give you a better experience
Backups are more scalable and provide a higher level of data protection and mobility. Depending upon the provider, backup software or service may follow varied methods such as:
- Full system backup – All system data.
- Incremental backup – Only new or modified data.
- Reverse Incremental backup –Mirroring technique, fastest and identical to a full backup, and takes the most space as the files are not compressed away to be stored.
- Differential backup – Cumulative replica of all the data changes only that were done since the last performed full system backup.
Backup systems are more proper for long term disaster and recovery.
Both snapshots and backups have their perks and must be seen individually.
With an excellent snapshot tool, you may decide how much storage you want to use for snapshots. Snapshots are quick to save and prompt in restoring and great at versioning.
Backups are excellent at securing data in the long run. They may take a considerably vast storage space but are independent of the system failure. They protect you better from a system or drive failure and malware.
Snapshot can be used as a part of backup but should not be considered as an actual database backup.
The snapshot itself alone cannot replace backup. Nowadays, database backup and recovery services are the combinations of the two.
Backups work well with technologies like snapshot and replication, for overall database support and security in an organization.
You May Also Like To Read
Top Open Source Data Recovery Software