Virtualization
Virtualization splits a single physical computer into multiple “virtual” servers. The virtual machines (VMs) operate on the dedicated hardware without depending on each other.
With virtualization, you split a single physical system into various independent environments, known as virtual machines. It helps you create multiple computer simulations with dedicated resources from the host hardware.
The server based system architecture (SBSA) capabilities are identical to the host system with the help of a hypervisor or the Virtual machine monitor (VMM).
Virtualization is far more capable and has multiple levels of implementation.
Emulation
Emulation is a concept of creating an environment that imitates the properties of one system onto another.
An Emulator mimics the qualities and logic of one processor to run in another platform efficiently.
Emulation is an excellent way to run an OS or software in any other system. Guest Operators need a translation.
Emulation brings higher overhead but has its perks too. It is highly inexpensive, easy to access, and helps us run the programs that have become obsolete in the available system.
An emulator converts the needed architecture CPU instructions and successfully runs it on another architecture.
Anyone can access the emulation platforms remotely and is easier to use. It is an excellent ability to have for embedded/OS development, without affecting the underlying OS.
Emulation can generally handle the size of the design under test (DUT), without considering the host’s capabilities.
Also Read: Implementation Levels of Virtualization Explained
The Main Difference Between Virtualization and Emulation
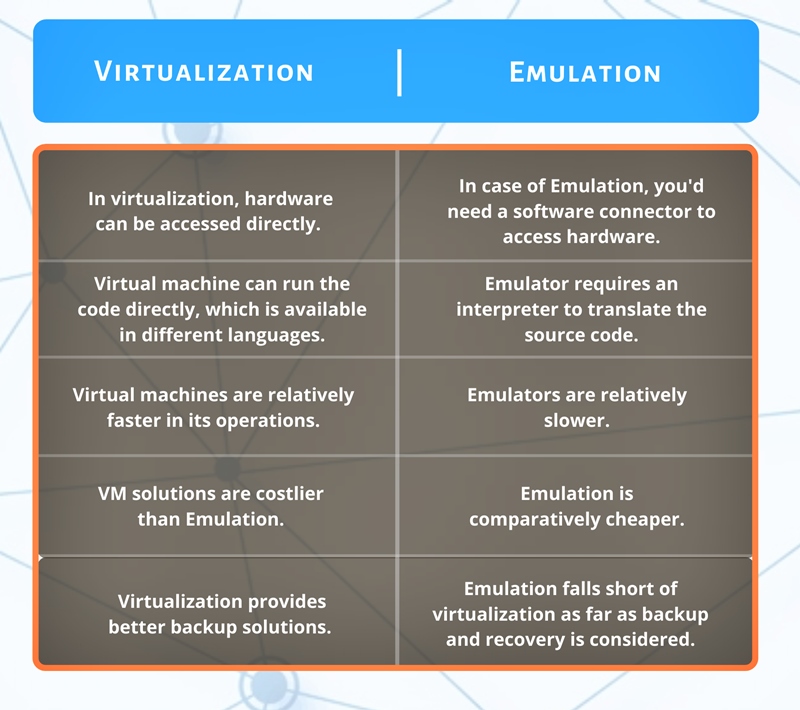
Unlike in virtualization, the emulation process requires a software bridge. In virtualization, you can directly access the hardware.
The main difference between the virtual machine and emulator is that the virtual machine runs code directly with a different set of domains in use language.
The basic emulation requires an interpreter. This interpreter translates the source code and converts it to the host system’s readable format, to further process it.
Whereas, in an emulator, the guest operating system does not run on the physical hardware. Emulators are slow in comparison to the Virtual Machines. Emulators do not rely on CPU while the VMs make use of CPU.
Unlike Emulation, Virtualization puts a layer between hardware physically to control access to it. This helps in resource sharing amongst guest machines as the virtualization gives you access to the host resources.
The virtual machines use the central system’s resources directly. Also, the VM solution is costlier and more complex than the emulation technique. But the virtualization provides more throughput and minimal overhead with a better backup and recovery solution.
Also Read: Things to Consider for Virtualization Disaster Recovery
Virtualization Vs. Emulation Comparison in Tabular Form
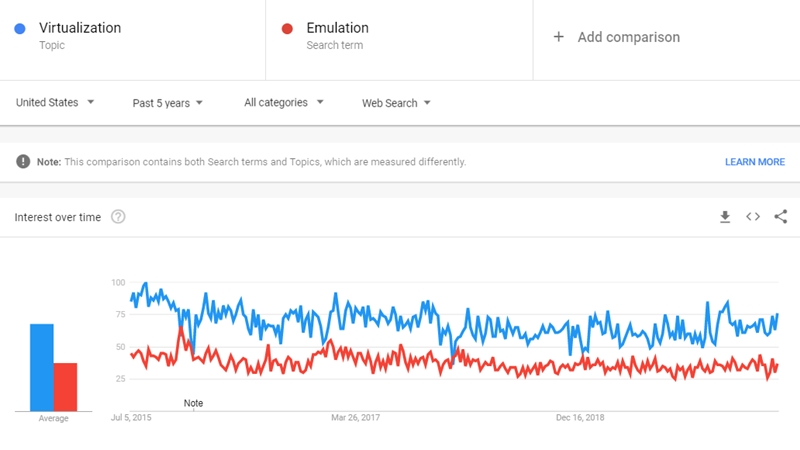
Virtualization and Emulation Popularity Comparison
The graph below displays the popularity trends of Virtualization and Emulation over Google search in the last 5 years, within the U.S.
Conclusion
You may get puzzled between the two, as the word “Emulation” is also used in server virtualization to describe a virtual environment.
In emulation, you use full hardware and software that you want to imitate on top of the host system. In virtualization, you mimic the only parts of the hardware according to your requirements with the help of guest OS to run correctly to have the same architecture.
The main similarity between virtualization and emulation is they both are programs that imitate hardware one way or another. They both let you mimic and run a program in one environment that is actually meant for the other but with different techniques.
Virtualization and Emulation methods provide you with solutions to deploy multiple isolated services without going on a different platform. Both are used to meet a different set of expectations and are on a different level. They should not be mistaken for each other.
You May Also Like to Read:
What are the Pros and Cons of Virtualization?