Imagine you watch an artist create paintings for years. Eventually, you learn their style so well that you can paint something new that looks like their work. This is the heart of a generative model – it studies patterns in existing content and then creates fresh material that follows those same patterns.
These systems learn the hidden rules behind everything from writing styles to visual compositions. After analyzing thousands of examples, they can produce original content that feels authentic to the source material. Think of it like a chef who, after tasting many cuisines, can create a new dish that captures familiar flavors in an original way.
The magic happens in how these systems balance following learned patterns while still introducing novelty. They’ve become remarkably good at tasks from writing business correspondence to designing graphics that look like they came from human hands. Let us learn the key concepts behind these models further.
What Is A Generative Model?
Generative models are a major group of statistical models in machine learning and are aimed at understanding the underlying probability distribution of the observed data. These models are able to approximate the joint probability distribution P (X, Y) or the marginal distribution P(X), thus allowing them to generate new samples that have a similar distribution to the training data.
At their core, these models are constructed upon principles of probabilistic inference and sampling theory. Alternative approaches include autoregressive models that decompose joint distributions using chain rule formulations and energy-based models that define probability densities through energy functions.
The mathematical foundation of these models typically involves maximum likelihood estimation, Bayesian inference, or other statistical learning frameworks. Evaluation of the efficacy of models can be made through metrics such as negative log-likelihood, Kullback-Leibler divergence, inception scores, or Fréchet inception distance.
Significance Of Generative Models:
Generative models represent a revolutionary step in the computational theory of learning. They make possible the creation of machines that can generate new examples, instances that are indistinguishable from the ones generated by nature.
This capacity fundamentally changes areas ranging from signal processing to computational biology by providing scaffolds for data augmentation, distribution modeling, and uncertainty quantification that were previously impossible through discriminative methods alone.
Generative frameworks are theoretically valuable because they explicitly address the problem of high-dimensional density estimation. By defining complex probability distributions, these models shed light on the manifold hypothesis, information geometry, and statistical physics interpretations of learning.
Their capacity to learn disentangled representations and generate counterfactual examples offers unprecedented approaches to interpretability, fairness, and causal reasoning. Moreover, their ability to model joint distributions facilitates complex conditional generation tasks that bridge multiple modalities and semantic levels of abstraction.
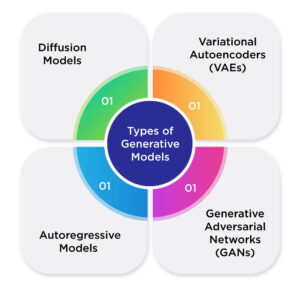
Types Of Generative Models:
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) represent a prominent class of these models that utilize an encoder-decoder architecture coupled with variational inference. These models encode input data into a lower-dimensional latent space with a defined probability distribution, typically Gaussian, and then decode samples from this space to generate new instances.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) implement a competitive framework between two neural networks—a generator that produces synthetic data and a discriminator that evaluates authenticity. This adversarial training process drives the generator to create increasingly convincing outputs while the discriminator becomes more discerning.
Autoregressive models decompose joint probability distributions into products of conditional probabilities, generating data sequentially, one element at a time. Notable implementations include NADE (Neural Autoregressive Density Estimator), PixelCNN for images, and transformers for text generation.
Diffusion models work by eventually adding noise to data and, after that, learning to reverse this process. Starting from pure noise, these models iteratively denoise to generate samples. This approach has yielded state-of-the-art results in image synthesis through implementations like DDPM (Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models) and score-based models, which estimate gradients of data distributions.
Examples Of Generative Models:
GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) exemplifies how autoregressive approaches excel in natural language domains. Their emergent capabilities include coherent narrative construction, code generation, and even reasoning tasks, demonstrating how scaled such models can internalize complex structural and semantic knowledge from training data.
WaveNet pioneered autoregressive approaches for raw audio waveform generation, producing remarkably natural speech and music samples. This architecture fundamentally transformed text-to-speech systems through its capacity to capture subtle acoustic nuances, breathing patterns, and contextual phonetic variations.
Jukebox extends modeling to music production through a hierarchical approach that captures structure at multiple timescales. This system generates novel compositions with coherent harmony, rhythm, and instrumentation. Its ability to incorporate lyrical conditioning demonstrates a sophisticated understanding of the relationship between textual and musical content.
Applications Of Generative Models
Digital Content Creation
Content creation is being revolutionized by generative methods. They allow for fast ideation from an initial sketch or description of the design. Fashion designers leverage these tools to visualize new collections, architects explore structural possibilities, and film studios generate concept art for pre-production.
Video Game Development
Video game development incorporates generative methodologies for procedural world-building, character customization, and dynamic narrative construction. These approaches enable studios to create vast, explorable environments with coherent ecological and architectural patterns without manual placement of every element.
Speech Synthesis
Speech synthesis applications employ generative frameworks to produce naturalistic vocal performances with appropriate prosody, emotional resonance, and contextual awareness. This technology enables personalized audiobook narration, multilingual communication aids for those with speech impairments, and voice restoration services.
Simulation for Autonomous Vehicles
Simulation environments for autonomous vehicle training utilize generative techniques to create diverse, photorealistic testing scenarios. These systems generate variations in lighting conditions, weather patterns, pedestrian behaviors, and traffic configurations to comprehensively evaluate decision-making algorithms.
Way Forward!
As generative models continue to progress with each passing day, they promise to redefine human-machine collaboration across creative and scientific domains. The future lies not in replacing human ingenuity but in amplifying it—creating tools that extend our cognitive capabilities while preserving the essential human elements of intuition, ethical judgment, and cultural understanding that give our creations meaning.
To learn more about such models, machine learning, and other similar technologies, visit us at HiTechNectar!
Read More:
What is GAN in Machine Learning? An Introduction to Generative Adversarial Network