Observability and monitoring are two crucial elements of DevOps, MLOps, and the process of integrating any advanced tools or technologies into a business model. These are two stages that help ensure appropriate software performance with lower risks. Though many professionals often get confused between observability and monitoring, both have different practices and goals to fulfil.
Businesses often fail to adopt effective observability and monitoring frameworks, though they bear major significance. Nevertheless, failure to adopt these two can result in system collapse and delayed risk detection. Such circumstances can lead to unsuccessful software and model development alongside their deployment.
Sources state that over 75% of software projects are at risk due to inappropriate monitoring and observability. So, let us understand how observability vs monitoring differs from each other and which one is more appropriate for your business.
What is Observability?
Observability is the practice of understanding what is happening inside a complex system by examining the data it generates- logs, metrics, and traces. The process does not involve extra tests or code. It gives teams a single view of applications, infrastructure, and dependencies so they can trace issues early, find root causes, and fix problems faster.
Observability tools aggregate and correlate telemetry, map interactions across services, and provide actionable insights that improve reliability, speed troubleshooting, keep user experiences smooth, and reduce downtime.
How does Observability Work?
Observability takes monitoring to the next level by shifting from reactive alerts to a proactive, holistic understanding of the system. While it uses the same telemetry data logs, metrics, and traces, it correlates all of it in real time to provide complete, contextual insights into system health.
With observability tools, DevOps teams, SREs, and IT operations can see not just what happened, but where it happened, why it happened, and how it impacts other parts of the environment. Observability platforms automatically map dependencies, discover new data sources like new API calls, and reveal how even the smallest change can affect distributed systems.
Unlike monitoring, which focuses on predefined issues, observability helps teams investigate unknown or unexpected problems. Many solutions now integrate machine learning and AIOps to make sense of large data volumes and prioritize issues by severity. This makes observability essential for debugging, optimizing performance, and maintaining reliability in modern cloud-based systems.
What is Monitoring?
Monitoring refers to the process of collecting, assessing, and using data from systems to analyze the program’s performance and guide it to meet its primary goals. It is generally adopted to track and measure program health alongside detecting anomalies. While detecting anomalies, monitoring also ensures preventing emerging risks while sustaining seamless operations.
Monitoring also serves as a key performance indicator (KPI) in DevOps, helping track performance and identify opportunities for improvement.
How Does Monitoring Work?
Monitoring is one of the oldest and most essential practices in managing IT systems. At its core, monitoring is reactive; it watches issues and alerts teams when something goes wrong. Monitoring tools collect telemetry data, including logs, metrics, and traces, to check if systems are performing within expected thresholds.
Teams define benchmarks, configure dashboards, and set up alerts based on this data. For example, if the time to deploy an application suddenly surges beyond the normal range, a monitoring tool will notify the team that there might be an issue. Monitoring also helps document system dependencies, so teams understand how components interact.
In DevOps, monitoring spans the entire software development lifecycle, and Application Performance Monitoring (APM) focuses specifically on the health and user experience of production applications.
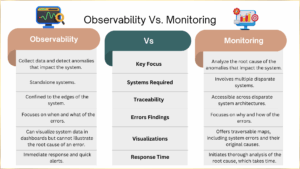
Observability vs Monitoring: Major Differences
Though observability vs monitoring are often considered to be similar processes, they have major differences. Let us discuss the key aspects that distinguish them-
Observability vs Monitoring: Which Approach is More Appropriate for Your Business?
Observability and monitoring are both essential and implemented for different purposes. In short, these are two unignorable stages in DevOps and IT Ops. Hence, a combined strategy will offer a more holistic and robust framework for system upliftment. While monitoring tracks the initial signs of an error, observability offers an extensive report of the error alongside the causes for it.
With a combined effort, errors will be identified and resolved quickly. Moreover, merging both will offer additional benefits, such as-
Faster Incident Response and Mitigation:
IT professionals and developers can eliminate their regular challenges more quickly than ever with effective incident response and mitigation.
Higher System Reliability and Uptime:
Since monitoring and observability help in tracing and fixing errors, they automatically assist in improving system performance and overall reliability.
Enhanced User Experience:
Improved performance, reliability, and fewer errors contribute to a higher user experience. IT professionals and developers will be able to complete the application development and deployment without significant disruption.
Heading Toward a Safer Tomorrow!
IT processes involve several risks that can lead to system disruption and project failures. For such reasons, a robust assessment framework is necessary, which not only identifies risks but also helps in mitigating them. Observability vs monitoring surely bears major differences, but combining them can offer a far sophisticated approach to safeguard system defenses.
Observability and monitoring further contribute to the successful development and deployment of software and AI models. Learn more about crucial technologies and strategies that can change your tech game with our informative blogs.
F&Qs:
Q1: What are the three pillars of observability?
Answer: Metrics, logs, and traces are the three pillars of observability.
Q2: What are the three main types of monitoring?
Answer: Result-oriented, constructivist, and reflexive are the three major types of monitoring.
You might like:
Everything to Know about DevOps Monitoring
Top 9 Open-source MLOps Tools